Geography
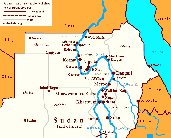
The land of Kush is part of the modern day country of Sudan. The phrase Ancient Nubia is commonly used by scholars as an alternative name for Kush. Historically, the land of Kush stretched roughly from Wadi Halfa in the north, to Kosti city (along the White Nile) and Sinnar city (along the Blue Nile) in the south; and from the Red Sea coast in the east, to Kordofan and the Libyan Desert in the west. It is important to note that historically there is a geographical distinction between Nubia and Kush. While the land of Kush is geographically restricted to Sudan, Nubia may be considered as encompassing parts of southern Egypt. (The identification of southern Egypt with Nubia is attributed to the expansion of a nomadic Nubian/Nobatan population which dates back to the third century CE.) Most of Sudan's topography is consisted of deserts, except for the narrow strip of the Nile valley which helped provide fertile agriculture and abundant pastures. Because of the availability of food and fresh water, the Nile Valley was populated more so than any other region in Sudan. The first civilization in Sudan, and one of the first in the world, developed there, along the Nile Valley.
Unlike the shorter stretch of Egypt's Nile Valley, some portions of Sudan's Nile Valley are not equally supportive of agriculture. As a result, pastoralism remains the dominant way of life in some of the dry areas of the Valley. Between Aswan and Wadi Halfa, in Lower Nubia, the Nile river cuts through a barren stretch of desert that is mostly not supportive for agriculture. Five cataracts interrupt the flow of the Nile from south of Aswan to little north of the city of Berber in central Sudan. This makes sailing along the Nile impossible except for the short distances that separate between one cataract and the other. Agricultural lands are available in the Dongola Reach and along the curve of the Nile Valley as far south as Abu Hamed. This fertile region of the Nile Valley helped produced more than enough agricultural supply for the ancient civilization of Kush to develop.
Around the Dongola Reach and south in the Bayuda Desert are also plenty of pastoral lands. From Abu Hamed to the city of Berber in the south, the Nile valley is less productive. However, south of Berber, the Valley becomes fertile and supportive for extensive agriculture. There, in these more southerly areas of the Nile, prominent ancient Sudanese cities grew, such as Dangeil and Meroe. Immediately south of Khartoum, where the White and the Blue Niles converge, is the so-called land of el-Gezeera, which is Arabic for the island. This area is more fertile than any other region in North Sudan. The area of el-Gezeera is liable for extensive agriculture and has been supportive for human settlements sine ancient times. Prominent historical cities grew in el-Gazeera, such as the Funj city of Sinnar along the White Nile and the Kushite settlement of Kosti along the White Nile.
East of the Nile Valley is the Nubian Desert where agriculture is not possible. There along the Sudanese Red Sea coasts, the Beja formed their own communities depending mainly on pastoralism and subsistent agriculture in the more southerly regions of el-Butana, in the southeastern area of North Sudan. An ancient agricultural society known as the Gash-culture flourished there in el-Butana, along the Gash river. Also known as Punt, the people of this culture developed their own state out of trade in incense and exotic items. The Punites also traded with neighboring regions, including Kush and Egypt.
The Libyan Desert, west of Nubia, is consisted of flat arid lands and stretches of sand-dunes that continue, across the Sahara Desert of north and central Africa, all the way to the opposite side of the African continent. Extremely little rainfall occur in the Libyan Desert and only few regions and oasis are supportive for pastoral activities. South of the Libyan Desert and adjacent to the White Nile, is the region of Kordofan where the land is little more fertile and is supportive of subsistent agriculture. Communities flourished there growing crops every season. The youth of these communities annually crossed northward to safe areas of the Libyan Desert in search of pastures for their animals. |